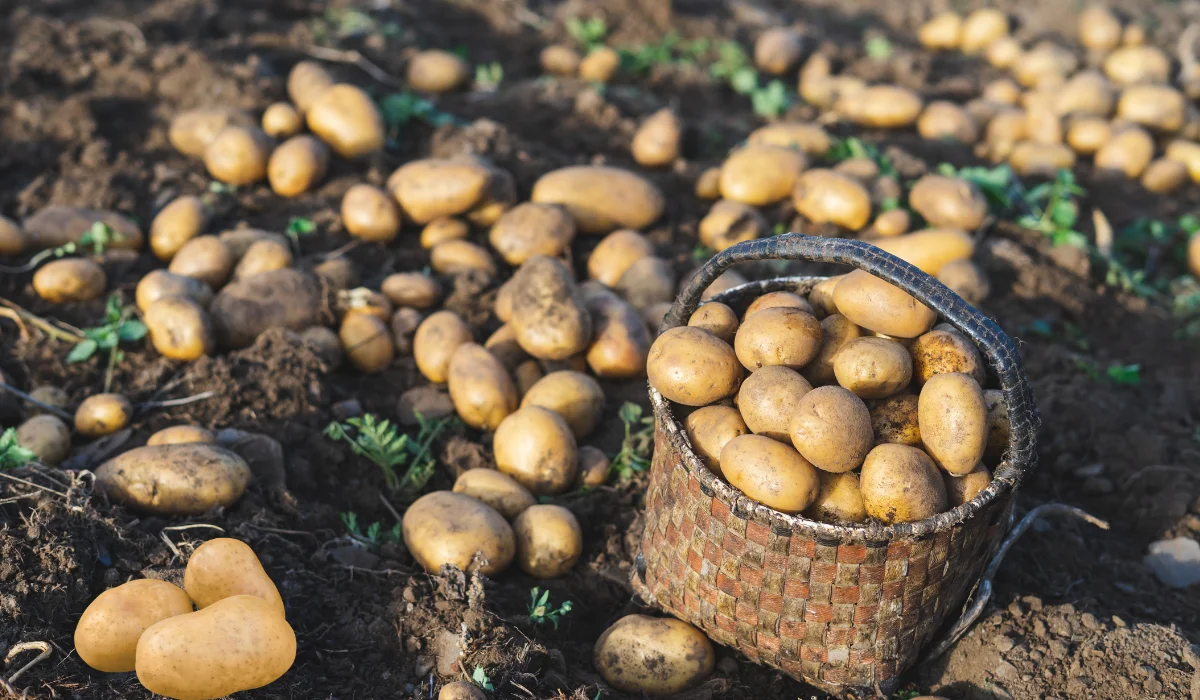
Potatoes, often dismissed as a starchy side dish, are a nutritional powerhouse deserving of greater recognition in the world of healthy eating. These humble tubers, originating from the Andean region of South America, have been a staple food for centuries and continue to play a vital role in diets across the globe. With a wide variety of types, including russet, red, yellow, purple, and fingerling, potatoes offer a versatile and nutrient-rich option for meals. This article delves into the nutritional benefits of potatoes, their impact on health, and how they can be incorporated into a balanced diet.
Macronutrients in Potatoes
Potatoes are primarily composed of carbohydrates, but they also provide a good amount of other essential macronutrients.
Carbohydrates
A medium-sized potato (about 150 grams) contains approximately 26 grams of carbohydrates. These carbohydrates are primarily in the form of starch, which serves as a valuable source of energy. Unlike refined carbohydrates, the starch in potatoes is complex, meaning it breaks down more slowly in the body, providing sustained energy and helping to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Dietary Fiber
Potatoes are also a good source of dietary fiber, particularly when consumed with the skin. A medium potato with skin can provide about 2 grams of fiber, which is essential for digestive health. Fiber aids in preventing constipation, lowering cholesterol levels, and controlling blood sugar. The resistant starch in potatoes acts similarly to fiber, offering additional benefits for gut health by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria in the colon.
Protein
While not a significant source of protein compared to legumes or meat, potatoes do contain some protein. A medium potato provides about 2-3 grams of protein, including all essential amino acids, making it a valuable component of a plant-based diet.
Fats
Potatoes are naturally low in fat, with less than 0.2 grams per medium-sized potato. This makes them an excellent choice for those looking to reduce fat intake without sacrificing fullness or flavor.
Vitamins and Minerals
Potatoes are packed with a variety of vitamins and minerals that contribute to overall health.
Vitamin C
A medium potato contains about 27 milligrams of vitamin C, which is roughly 30% of the daily recommended intake. Vitamin C is a potent antioxidant that boosts the immune system, aids in collagen production, and helps the body absorb iron from plant-based foods.
Potassium
Potatoes are an excellent source of potassium, with a medium potato providing around 620 milligrams. Potassium is crucial for maintaining healthy blood pressure, balancing electrolytes, and ensuring proper muscle and nerve function. In fact, potatoes have more potassium than bananas, which are often touted as the go-to potassium source.
Vitamin B6
A medium potato offers about 0.2 milligrams of vitamin B6, contributing to 10% of the daily recommended intake. Vitamin B6 is vital for brain health, aiding in neurotransmitter production and cognitive development. It also plays a role in protein metabolism and the creation of red blood cells.
Iron
Potatoes contain about 1.1 milligrams of iron per medium potato, which helps in the formation of hemoglobin and myoglobin, proteins that transport oxygen in the blood and muscles. Including potatoes in a diet can help prevent iron-deficiency anemia, especially when paired with vitamin C-rich foods that enhance iron absorption.
Magnesium
A medium potato provides about 48 milligrams of magnesium. This mineral is involved in over 300 biochemical reactions in the body, including energy production, muscle and nerve function, and the regulation of blood pressure.
Antioxidants and Phytochemicals
Beyond vitamins and minerals, potatoes are rich in antioxidants and phytochemicals that offer additional health benefits.
Polyphenols
Potatoes contain various polyphenols, which are natural compounds that have antioxidant properties. These compounds help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals, potentially reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders.
Carotenoids
Certain varieties of potatoes, particularly yellow and orange-fleshed ones, contain carotenoids such as lutein and zeaxanthin. These antioxidants are important for eye health, helping to protect against age-related macular degeneration and cataracts.
Anthocyanins
Purple and blue potatoes are rich in anthocyanins, pigments that have powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Research suggests that anthocyanins may help lower blood pressure, improve brain function, and reduce the risk of certain cancers.
Health Benefits of Potatoes
Given their rich nutritional profile, potatoes offer numerous health benefits when consumed as part of a balanced diet.
Weight Management
Contrary to popular belief, potatoes can be part of a weight management plan. They are low in calories and high in water content, which can help with satiety. The fiber and resistant starch in potatoes also contribute to a feeling of fullness, reducing overall calorie intake. It is important to prepare potatoes in a healthy manner, such as baking, boiling, or steaming, rather than frying, to keep the calorie count low.
Heart Health
The potassium, fiber, and antioxidants in potatoes contribute to cardiovascular health. Potassium helps regulate blood pressure, while fiber reduces cholesterol levels. The antioxidants in potatoes, particularly in colored varieties, help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, which are risk factors for heart disease.
Digestive Health
The fiber and resistant starch in potatoes support a healthy digestive system. Fiber helps prevent constipation by adding bulk to stool, while resistant starch acts as a prebiotic, feeding the beneficial bacteria in the gut. A healthy gut microbiome is linked to improved digestion, enhanced immune function, and a reduced risk of gastrointestinal diseases.
Blood Sugar Control
Despite being high in carbohydrates, potatoes can be part of a diabetic-friendly diet when consumed in moderation and prepared correctly. The fiber and resistant starch in potatoes help slow the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream, preventing spikes in blood sugar levels. Pairing potatoes with protein, healthy fats, and non-starchy vegetables can further help manage blood sugar levels.
Culinary Uses and Tips
Potatoes are incredibly versatile and can be prepared in numerous ways to suit various dietary needs and culinary preferences.
Boiled or Steamed
Boiling or steaming potatoes is a healthy preparation method that preserves most of their nutrients. These methods do not require added fats, making them ideal for those watching their calorie and fat intake.
Baked
Baking potatoes with the skin on is another nutritious option. The skin contains a significant amount of fiber and nutrients, so keeping it on enhances the nutritional value. Baked potatoes can be topped with healthy ingredients such as yogurt, chives, or a sprinkle of cheese.
Mashed
Mashed potatoes can be made healthier by using low-fat milk or broth instead of heavy cream and butter. Adding garlic, herbs, or roasted vegetables can boost flavor and nutrition.
Roasted
Roasting potatoes with a small amount of olive oil and herbs is a delicious and nutritious way to enjoy them. Roasting brings out the natural sweetness of the potatoes and adds a satisfying crispy texture.
Salads
Potato salads can be made healthier by using vinaigrette dressings instead of mayonnaise-based ones. Adding a variety of vegetables, such as bell peppers, cucumbers, and tomatoes, increases the nutritional value and adds flavor.
Conclusion
Potatoes are a nutrient-dense food that offers numerous health benefits. They are a rich source of carbohydrates, fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, making them an excellent addition to a balanced diet. When prepared in healthy ways, potatoes can support weight management, heart health, digestive health, and blood sugar control. Embracing the versatility of potatoes and incorporating them into various dishes can enhance both the nutritional value and the enjoyment of meals. So next time you're planning a meal, consider the humble potato as a nutritious and delicious option.

 English
English